Space, often referred to as the “final frontier,” has long captured the imagination and curiosity of humans. From the earliest civilizations, humans have looked up at the stars and wondered what lies beyond the limits of our planet. The desire to explore and understand the universe has driven countless scientific discoveries and technological innovations, and has inspired countless works of art, literature, and film.
Today, the exploration of space has become an increasingly important and ambitious endeavor, with space agencies and private companies working to develop the technologies and infrastructure needed to support human settlements in space. The potential rewards of space exploration are vast, and include the possibility of making new scientific discoveries, discovering new resources, and establishing a backup location for human civilization in the event of a catastrophic event on Earth.
Space Colonization
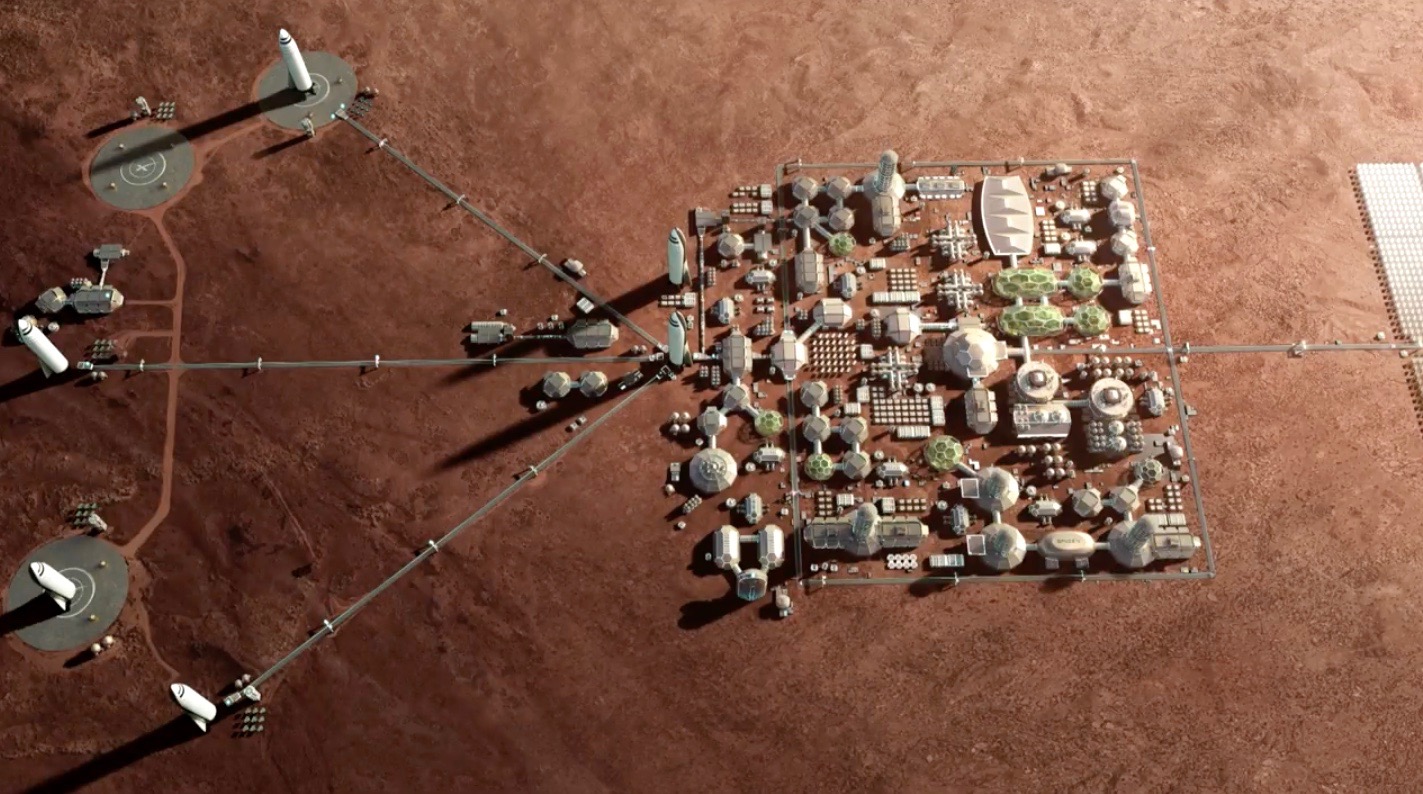
Space colonization, also known as space settlement or space habitation, refers to the concept of establishing permanent or semi-permanent human communities on other celestial bodies, such as the Moon, Mars, or other planets or moons in the solar system. The ultimate goal of space colonization is to make it possible for humans to live and work in space for extended periods of time, eventually creating self-sustaining and autonomous communities that can thrive independently of Earth.

There are several motivations for space colonization.
One of the main motivations for space colonization is the desire to explore and understand the universe. By establishing human settlements on other celestial bodies, we can gain insights into the history, geology, and potential for life on these bodies, as well as learn more about the conditions necessary for human survival in space.
Another motivation for space colonization is the search for new resources. Many celestial bodies in our solar system, such as the Moon and asteroids, are thought to contain valuable resources such as water, minerals, and rare earth elements, which could be used to support human settlements or be brought back to Earth for use. For example, the Moon is thought to contain large deposits of helium-3, a rare isotope that could potentially be used as a fuel for fusion reactions.
Space colonization could also serve as a backup location for human civilization in the event of a catastrophic event on Earth. This could include natural disasters, such as a supervolcano eruption or a large asteroid impact, or man-made disasters, such as nuclear war or environmental collapse. By establishing human settlements on other celestial bodies, we could ensure the survival and continuity of human civilization in the face of such threats.
In addition to these motivations, space colonization could also provide a solution to issues such as overpopulation and resource depletion on Earth. By establishing human settlements on other celestial bodies, we could alleviate pressure on Earth’s resources and create new opportunities for economic growth and development.
Space exploration and colonization challenges
One major challenge to space colonization is the high cost of space travel. The development and operation of spacecraft and other space-related infrastructure is a costly and complex endeavor, and it is not yet clear how space colonization could be made financially viable on a large scale. Another challenge is the harsh environmental conditions of space, which can be deadly to humans without proper protective measures. The lack of a protective atmosphere, the extreme temperatures, the high levels of radiation, and the lack of access to basic necessities such as food, water, and oxygen all present significant obstacles to the establishment of permanent human settlements in space.
To address these challenges, there have been efforts to develop technologies and strategies that could support space colonization. One approach is the use of in-situ resource utilization (ISRU), which involves using resources found on other celestial bodies, such as water and minerals, to support human settlements. Another approach is the development of closed-loop life support systems, which recycle and reuse resources such as water and oxygen to support human life.
Despite the challenges, space colonization is an exciting and ambitious goal that has the potential to transform the human experience and expand our understanding of the universe. As we continue to make progress in developing the technologies and strategies needed to establish and sustain human settlements in space, it is likely that we will see more and more people living and working in space in the future.
Space exploration and blueprint rocket science
Rocket science is one of the key space exploration technologies, involving the design, construction, and operation of rockets and other spacecraft. Rockets are used to launch payloads, such as satellites and spacecraft, into space, and are an essential component of space exploration.
Rockets work by using a fuel and an oxidizer to create a chemical reaction that generates hot gases. These gases are expelled through a nozzle at the bottom of the rocket, creating a force that propels the rocket upwards. The greater the force of the gas expulsion, the faster the rocket will travel.
Rockets come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and are classified based on the type of fuel and oxidizer they use. Solid rockets, for example, use a solid fuel and an oxidizer, while liquid rockets use a liquid fuel and an oxidizer. Hybrid rockets use a combination of solid and liquid fuels.
The development of rocket technology has been an ongoing process, with significant advances being made over the course of the 20th and 21st centuries. One of the key pioneers in rocket science was the German physicist and engineer, Wernher von Braun, who developed the V-2 rocket for the Nazi military during World War II and later played a key role in the development of the Saturn V rocket for NASA’s Apollo program.
Today, rocket science is a highly advanced field, with numerous private companies and space agencies working on the development of new rockets and spacecraft. These include companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin, which are working on reusable rockets and spacecraft that could make space travel more affordable and accessible.
Is it even possible, considering the role of the creator of the universe?
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that the concept of space colonization is inherently impossible or contrary to the will of a hypothetical creator of the universe. Space colonization is a complex and ambitious goal that would require significant technological, logistical, and financial resources, but it is not inherently impossible.
The possibility of space colonization depends on a variety of factors, including the availability of resources, the development of technologies and infrastructure to support human settlements in space, and the willingness and ability of humans to explore and settle other celestial bodies. While there are many challenges and uncertainties involved in space colonization, it is ultimately up to humans to decide whether or not to pursue this goal, and what steps to take to achieve it.
It is worth noting that the concept of a creator of the universe is a philosophical or religious belief that is outside the purview of science. Scientific inquiries are based on evidence and empirical observation, and do not address questions of supernatural causation or divine intervention.
Philosophical objection on expending massive resources and money
Some people may have philosophical or theological objections to the idea of space colonization.
One potential philosophical objection to space colonization is the argument that it is wasteful or irresponsible to devote significant resources to exploring and settling other celestial bodies when there are still pressing problems to be addressed on Earth. Some people may argue that it is more important to focus on issues such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation, rather than investing in space exploration.
Another philosophical objection to space colonization may be based on the idea that it is unnatural or unethical to alter other celestial bodies or to introduce human life into environments where it does not naturally occur. Some people may argue that it is important to preserve the natural integrity of other planets and moons, and that human intervention could have unintended consequences.
From a theological perspective, some people may argue that space colonization is contrary to the will of the creator of the universe, or that it represents an attempt to play God by altering the natural order of the universe. Others may view space colonization as a way of fulfilling a divine mandate to explore and understand the universe, and may see it as a way of expressing reverence and awe for the creator.
Space exploration acheivements.
Space exploration has achieved many notable milestones and achievements over the course of its history. Some of the most significant achievements include:
- 1957: The Soviet Union launches Sputnik 1, the first successful satellite.
- 1961: Yuri Gagarin becomes the first human to travel to space, completing one orbit around the Earth in his spacecraft, Vostok 1.
- 1969: NASA’s Apollo 11 mission successfully lands astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin on the Moon, fulfilling President John F. Kennedy’s goal of landing a man on the Moon by the end of the 1960s.
img src – space.com - 1971: The Soviet Union’s Mars 3 spacecraft becomes the first spacecraft to land on Mars.
- 1972: NASA’s Pioneer 10 spacecraft becomes the first spacecraft to fly past Jupiter.
- 1976: NASA’s Viking 1 and 2 landers successfully land on Mars and conduct the first experiments on the surface of the planet.
- 1981: NASA’s space shuttle program begins, allowing for the reuse and repair of spacecraft in space.
- 1988: The first components of the International Space Station (ISS) are launched into orbit.
- 2001: The first crew of the ISS, including American astronaut Bill Shepherd and Russian cosmonauts Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko, arrive at the station.
- 2004: NASA’s Spirit rover successfully lands on Mars and begins exploring the planet’s surface.
- 2020: NASA’s Artemis program is launched, with the goal of sending humans back to the Moon by 2024 and establishing a permanent presence on the lunar surface.
Private industry has played an increasingly important role in space exploration in recent years, with companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic making significant achievements in the field.
Some examples of private industry achievements in space exploration include:
- 2002: SpaceX is founded by entrepreneur Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs and enabling the colonization of Mars.
- 2004: SpaceShipOne, developed by aerospace manufacturer Scaled Composites, becomes the first privately-funded spacecraft to reach outer space, winning the $10 million Ansari X Prize.
- 2008: SpaceX becomes the first private company to send a spacecraft, the Falcon 1, to the International Space Station (ISS).
- 2011: SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft becomes the first privately-developed spacecraft to be launched to and from the ISS.
- 2015: Blue Origin, a spaceflight company founded by Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, successfully lands its New Shepard spacecraft after reaching space.
- 2018: SpaceX launches the Falcon Heavy, the most powerful rocket in operation at the time, and successfully lands two of its first stage boosters.
- 2020: SpaceX launches its Crew Dragon spacecraft, becoming the first private company to send humans to the ISS.
- 2020: Virgin Galactic, a spaceflight company founded by entrepreneur Richard Branson, successfully launches its SpaceShipTwo spacecraft to the edge of space, carrying its first paying customers.
Despite the many challenges and risks involved in space exploration, human curiosity and the desire to push the boundaries of what is possible have driven us to continually seek out new frontiers and explore the unknown. As we continue to make progress in space exploration, it is likely that we will continue to be inspired by the endless possibilities and mysteries of the universe.
